USA: Cars and Light-Duty Trucks: California
- Introduction
- Low Emission Vehicle (LEV) Standards
- Low Emission Vehicle II (LEV II) Standards
- Low Emission Vehicle III (LEV III) Standards
- Low Emission Vehicle IV (LEV IV) Standards
Introduction
California emission standards have been traditionally more stringent than the EPA requirements, but their structure is similar to that of the federal regulations. The major regulatory steps in the evolution of California emission standards include:
- Tier 1/LEV emission standards that extended through the year 2003.
- LEV II emission standards were phased-in through model years 2004-2010.
- LEV III emission standards are phased-in through model years 2015-2025. The LEV III program is a part of the Advanced Clean Cars (ACC) regulation.
- LEV IV emission standards are phased-in through model years 2026-2030. The LEV IV program is a part of the Advanced Clean Cars II (ACC II) regulation.
A number of other states, so-called ‘Section 177 States’, have adopted California emission standards.
Low Emission Vehicle (LEV) Standards
These California emission standards, which applied through model year 2003, were expressed using the following emission categories:
- Tier 1
- Transitional Low Emission Vehicles (TLEV)
- Low Emission Vehicles (LEV)
- Ultra Low Emission Vehicles (ULEV)
- Super Ultra Low Emission Vehicles (SULEV)
- Zero Emission Vehicles (ZEV)
Car manufacturers were required to produce a percentage of vehicles certified to increasingly more stringent emission categories, according to schedules based on vehicle fleet emission averages for each manufacturer. After 2003, Tier 1 and TLEV standards were eliminated as available emission categories.
The same standards for gaseous pollutants applied to diesel- and gasoline-fueled vehicles. PM standards applied to diesel vehicles only. Emissions were measured over the FTP-75 test and are expressed in g/mile. The additional SFTP procedures were phased-in in California between 2001 and 2005.
| Category | 50,000 miles/5 years | 100,000 miles/10 years | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMOGa | CO | NOx | PM | HCHO | NMOGa | CO | NOx | PM | HCHO | |
| Passenger cars | ||||||||||
| Tier 1 | 0.25 | 3.4 | 0.4 | 0.08 | - | 0.31 | 4.2 | 0.6 | - | - |
| TLEV | 0.125 | 3.4 | 0.4 | - | 0.015 | 0.156 | 4.2 | 0.6 | 0.08 | 0.018 |
| LEV | 0.075 | 3.4 | 0.2 | - | 0.015 | 0.090 | 4.2 | 0.3 | 0.08 | 0.018 |
| ULEV | 0.040 | 1.7 | 0.2 | - | 0.008 | 0.055 | 2.1 | 0.3 | 0.04 | 0.011 |
| LDT1, LVW <3,750 lbs | ||||||||||
| Tier 1 | 0.25 | 3.4 | 0.4 | 0.08 | - | 0.31 | 4.2 | 0.6 | - | - |
| TLEV | 0.125 | 3.4 | 0.4 | - | 0.015 | 0.156 | 4.2 | 0.6 | 0.08 | 0.018 |
| LEV | 0.075 | 3.4 | 0.2 | - | 0.015 | 0.090 | 4.2 | 0.3 | 0.08 | 0.018 |
| ULEV | 0.040 | 1.7 | 0.2 | - | 0.008 | 0.055 | 2.1 | 0.3 | 0.04 | 0.011 |
| LDT2, LVW >3,750 lbs | ||||||||||
| Tier 1 | 0.32 | 4.4 | 0.7 | 0.08 | - | 0.40 | 5.5 | 0.97 | - | - |
| TLEV | 0.160 | 4.4 | 0.7 | - | 0.018 | 0.200 | 5.5 | 0.9 | 0.10 | 0.023 |
| LEV | 0.100 | 4.4 | 0.4 | - | 0.018 | 0.130 | 5.5 | 0.5 | 0.10 | 0.023 |
| ULEV | 0.050 | 2.2 | 0.4 | - | 0.009 | 0.070 | 2.8 | 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.013 |
|
a - NMHC for all Tier 1 standards Abbreviations: LVW - loaded vehicle weight (curb weight + 300 lbs) LDT - light-duty truck NMOG - non-methane organic gases HCHO - formaldehyde | ||||||||||
Emission standards for medium-duty vehicles are summarized in Table 2.
| Category | 50,000 miles/5 years | 120,000 miles/11 years | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMOGa | CO | NOx | PM | HCHO | NMOGa | CO | NOx | PM | HCHO | |
| MDV1, 0-3750 lbs | ||||||||||
| Tier 1 | 0.25 | 3.4 | 0.4 | - | - | 0.36 | 5.0 | 0.55 | 0.08 | - |
| LEV | 0.125 | 3.4 | 0.4 | - | 0.015 | 0.180 | 5.0 | 0.6 | 0.08 | 0.022 |
| ULEV | 0.075 | 1.7 | 0.2 | - | 0.008 | 0.107 | 2.5 | 0.3 | 0.04 | 0.012 |
| MDV2, 3751-5750 lbs | ||||||||||
| Tier 1 | 0.32 | 4.4 | 0.7 | - | - | 0.46 | 6.4 | 0.98 | 0.10 | - |
| LEV | 0.160 | 4.4 | 0.4 | - | 0.018 | 0.230 | 6.4 | 0.6 | 0.10 | 0.027 |
| ULEV | 0.100 | 4.4 | 0.4 | - | 0.009 | 0.143 | 6.4 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 0.013 |
| SULEV | 0.050 | 2.2 | 0.2 | - | 0.004 | 0.072 | 3.2 | 0.3 | 0.05 | 0.006 |
| MDV3, 5751-8500 lbs | ||||||||||
| Tier 1 | 0.39 | 5.0 | 1.1 | - | - | 0.56 | 7.3 | 1.53 | 0.12 | - |
| LEV | 0.195 | 5.0 | 0.6 | - | 0.022 | 0.280 | 7.3 | 0.9 | 0.12 | 0.032 |
| ULEV | 0.117 | 5.0 | 0.6 | - | 0.011 | 0.167 | 7.3 | 0.9 | 0.06 | 0.016 |
| SULEV | 0.059 | 2.5 | 0.3 | - | 0.006 | 0.084 | 3.7 | 0.45 | 0.06 | 0.008 |
| MDV4, 8501-10,000 lbs | ||||||||||
| Tier 1 | 0.46 | 5.5 | 1.3 | - | 0.028 | 0.66 | 8.1 | 1.81 | 0.12 | - |
| LEV | 0.230 | 5.5 | 0.7 | - | 0.028 | 0.330 | 8.1 | 1.0 | 0.12 | 0.040 |
| ULEV | 0.138 | 5.5 | 0.7 | - | 0.014 | 0.197 | 8.1 | 1.0 | 0.06 | 0.021 |
| SULEV | 0.069 | 2.8 | 0.35 | - | 0.007 | 0.100 | 4.1 | 0.5 | 0.06 | 0.010 |
| MDV5, 10,001-14,000 lbs | ||||||||||
| Tier 1 | 0.60 | 7.0 | 2.0 | - | - | 0.86 | 10.3 | 2.77 | 0.12 | - |
| LEV | 0.300 | 7.0 | 1.0 | - | 0.036 | 0.430 | 10.3 | 1.5 | 0.12 | 0.052 |
| ULEV | 0.180 | 7.0 | 1.0 | - | 0.018 | 0.257 | 10.3 | 1.5 | 0.06 | 0.026 |
| SULEV | 0.090 | 3.5 | 0.5 | - | 0.009 | 0.130 | 5.2 | 0.7 | 0.06 | 0.013 |
| a - NMHC for all Tier 1 standards
Abbreviations: MDV - medium-duty vehicle (the maximum GVW from 8,500 to 14,000 lbs). The MDV category is divided into five classes, MDV1 .. MDV5, based on vehicle test weight. The definition of “test weight” in California is identical to the Federal ALVW. NMOG - non-methane organic gases HCHO - formaldehyde |
||||||||||
Low Emission Vehicle II (LEV II) Standards
In November 1998, the California ARB adopted LEV II emission standards which were phased-in from 2004 through 2010. Manufacturers may certify vehicles to LEV II emission standards (categories) until model year 2019.
Under the LEV II regulation, the light-duty truck and medium-duty vehicle categories of below 8500 lbs gross weight were reclassified and had to meet passenger car requirements, as shown in Table 3. As a result, most pick-up trucks and sport utility vehicles (old MDV4 and MDV5) were required to meet the passenger car emission standards. The reclassification was phased-in by the year 2007.
Three sets of increasingly more stringent emission standards were defined: LEV, ULEV, and SULEV. A fourth emission category, PZEV (partial zero emission vehicle), had the same test emission levels as SULEV, but also included a “zero” evaporative emissions standard and a 150,000 mile/15 years emission durability. LEV II emission standards for FTP-75 testing are summarized in the following tables (additional SFTP standards are also applicable).
| Category | 50,000 miles/5 years | 120,000 miles/11 years | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMOG | CO | NOx | PM | HCHO | NMOG | CO | NOx | PM | HCHO | |
| LEV | 0.075 | 3.4 | 0.05 | - | 0.015 | 0.090 | 4.2 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.018 |
| ULEV | 0.040 | 1.7 | 0.05 | - | 0.008 | 0.055 | 2.1 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.011 |
| SULEV | - | - | - | - | - | 0.010 | 1.0 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.004 |
| Weight (GVW) | Category | NMOG | CO | NOx | PM | HCHO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8,500 - 10,000 lbs | LEV | 0.195 | 6.4 | 0.2 | 0.12 | 0.032 |
| ULEV | 0.143 | 6.4 | 0.2 | 0.06 | 0.016 | |
| SULEV | 0.100 | 3.2 | 0.1 | 0.06 | 0.008 | |
| 10,001 - 14,000 lbs | LEV | 0.230 | 7.3 | 0.4 | 0.12 | 0.040 |
| ULEV | 0.167 | 7.3 | 0.4 | 0.06 | 0.021 | |
| SULEV | 0.117 | 3.7 | 0.2 | 0.06 | 0.010 |
Under the LEV II legislation, NOx and PM standards for all emission categories were significantly tightened compared to the LEV levels. The same standards applied to all vehicles regardless of fuel (under revisions adopted on November 15, 2001 gasoline vehicles have been no longer exempted from the PM standard). Light-duty LEVs and ULEVs certified to a 0.05 g/mi NOx standard, phased-in starting with the 2004 model year. A full useful life PM standard of 0.010 g/mi was introduced for light-duty vehicles and trucks less than 8500 lbs GVW certifying to LEV, ULEV, and SULEV standards. Therefore, the LEV II emission standards could only be met by vehicles with advanced emission control technologies. In the case of diesels, vehicles typically required particulate filters and NOx reduction catalysts.
Fleet Emission Requirements. LEV II standards required automakers to reduce their vehicle fleet emission levels each year through 2010—the last year of the LEV II phase-in period. In the case of light-duty vehicles, manufacturers had to meet increasingly tighter fleet average NMOG standards. For example, the final (2010) LEV II fleet average NMOG standard was 0.035 g/mi for PC/LDT1 and 0.043 g/mi for LDT2. Medium-duty vehicles had no fleet average standards, but manufacturers were required to certify increasing percentages of their MDVs to the applicable emission standards. Evaporative emission standards were also increasingly tightened through 2010.
While the California LEV II program was similar in structure to the federal Tier 2 regulation, there were a number of differences regarding overall fleet emission stringency, durability, and categorization of vehicles. One difference is that the federal approach uses eight certification “bins” (with Tier 2 Bin 5 being similar to California’s LEV, and Tier 2 Bin 2 similar to SULEV) to allow averaging across a greater level of emission diversification in the fleet. Another important difference is that, when fully implemented in 2010, the federal fleet average NMOG emissions—around 0.090 g/mi, based on Bin 5—can be more than twice as high the LEV II NMOG levels.
Table 5 shows the percentage breakdown of vehicles certified to the various emission categories—based on NMOG certification—in model year 2008. As apparent from the data, average new vehicles in 2008 were approximately regulated at ULEV NMOG levels.
| Category | LEV | ULEV | SULEV* | Sales Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC/LDT1 | 18% | 50% | 32% | 1,028,000 |
| LDT2 | 30% | 66% | 4% | 560,000 |
| MDV | 35% | 65% | 0% | 29,000 |
| Total | 23% | 55% | 22% | 1,618,000 |
| * Includes PZEV, which accounted for 92% of the SULEV+PZEV category | ||||
Low Emission Vehicle III (LEV III) Standards
The LEV III emission standards—adopted in January 2012 and amended in December 2012 [2946]—are phased-in over the 2015-2025 model years. Manufacturers can certify vehicles to the LEV III standards before model year 2015. Beginning with model year 2020, all vehicles must be certified to LEV III standards.
The LEV III standards modify the LEV II standards in several ways: (1) combine NMOG and NOx standards into one NMOG+NOx standard, (2) introduce a more stringent combined NMOG+NOx fleet average requirement for 2015-2025 model years, (3) add several emission standard bins, and (4) increase the durability requirements for emission control systems.
LEV III emission categories and their FTP-75 standards for light- and (chassis-certified) medium-duty vehicles are listed in Table 6. The numeric portion of the category name is the corresponding NMOG+NOx value in mg/mi.
| Vehicle Type | Emission Category | NMOG+NOx | CO | HCHO | PM† |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/mi | g/mi | mg/mi | g/mi | ||
| All PCs LDTs ≤ 8500 lbs GVWa All MDPVs |
LEV160 | 0.160 | 4.2 | 4 | 0.01 |
| ULEV125 | 0.125 | 2.1 | 4 | 0.01 | |
| ULEV70 | 0.070 | 1.7 | 4 | 0.01 | |
| ULEV50 | 0.050 | 1.7 | 4 | 0.01 | |
| SULEV30 | 0.030 | 1.0 | 4 | 0.01 | |
| SULEV20 | 0.020 | 1.0 | 4 | 0.01 | |
| MDVs 8501 - 10,000 lbs GVWb | LEV395 | 0.395 | 6.4 | 6 | 0.12 |
| ULEV340 | 0.340 | 6.4 | 6 | 0.06 | |
| ULEV250 | 0.250 | 6.4 | 6 | 0.06 | |
| ULEV200 | 0.200 | 4.2 | 6 | 0.06 | |
| SULEV170 | 0.170 | 4.2 | 6 | 0.06 | |
| SULEV150 | 0.150 | 3.2 | 6 | 0.06 | |
| MDVs 10,001 - 14,000 lbs GVWb | LEV630 | 0.630 | 7.3 | 6 | 0.12 |
| ULEV570 | 0.570 | 7.3 | 6 | 0.06 | |
| ULEV400 | 0.400 | 7.3 | 6 | 0.06 | |
| ULEV270 | 0.270 | 4.2 | 6 | 0.06 | |
| SULEV230 | 0.230 | 4.2 | 6 | 0.06 | |
| SULEV200 | 0.200 | 3.7 | 6 | 0.06 | |
|
† - Applicable only to vehicles not included in the phase-in of the final PM standards (Table 7 & Table 8). a - Loaded vehicle weight (LVW) b - Adjusted loaded vehicle weight (ALVW) Abbreviations: PC - Passenger car LDT - light-duty truck MDPV - medium-duty passenger vehicle MDV - medium-duty vehicle | |||||
SFTP and other testing requirements and standards, not shown in the table, are also applicable (for instance, HWFET and Cold CO standards).
Particulate Matter Standards. The PM emission standards shown in Table 6 will be tightened to much more stringent levels listed in Table 7. The phase-in schedule for LEV III PM standards is shown in Table 8 (the numbers denote the percentage of manufacturer’s vehicle fleet that must be certified to a given standard).
| Vehicle Type | PM Limit | Phase-in |
|---|---|---|
| mg/mi | ||
| PCs, LDTs, MDPVs | 3 | 2017-2021 |
| 1 | 2025-2028 | |
| MDVs 8501-10,000 lbs | 8 | 2017-2021 |
| MDVs 10,001-14,000 lbs | 10 | 2017-2021 |
| Year | PC, LDT, MDPV | MDV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM = 3 mg/mi | PM = 1 mg/mi | PM = 8/10 mg/mi | |
| 2017 | 10 | 0 | 10 |
| 2018 | 20 | 0 | 20 |
| 2019 | 40 | 0 | 40 |
| 2020 | 70 | 0 | 70 |
| 2021 | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| 2022 | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| 2023 | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| 2024 | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| 2025 | 75 | 25 | 100 |
| 2026 | 50 | 50 | 100 |
| 2027 | 25 | 75 | 100 |
| 2028 | 0 | 100 | 100 |
The SFTP limits for PM are 10 mg/mi for all PCs and for LDT1s (0-3750 lbs LVW), and 20 mg/mi for LDT2s (3751-8500 lbs LVW).
The more stringent standards have been adopted to ensure there is no increase in PM emissions from future engine technologies and that particulate filters are used on all diesel engines. In gasoline direct-injection engines, the future PM standards may trigger the use of gasoline particulate filters.
The LEV III proposal also included a particulate emission compliance option using a solid particle number (SPN) limit that was withdrawn from the final regulation. The proposed limit was 3 × 1012 1/mi. SPN emissions were to be measured over the FTP-75 cycle using a sampling approach patterned after the European PMP method.
Fleet Emission Requirements. New, stringent fleet emission requirements are phased-in, with the light-duty vehicle fleet reaching a SULEV-equivalent fleet average NMOG+NOx emission level of 0.030 g/mi in model year 2025 (Figure 1). Based on the emission certification and sales volume figures from Table 5, the average NMOG+NOx emissions in 2008 were 0.112 g/mi. Therefore, the LEV III fleet average requirements will result in a 73% reduction of NMOG+NOx emissions by 2025.
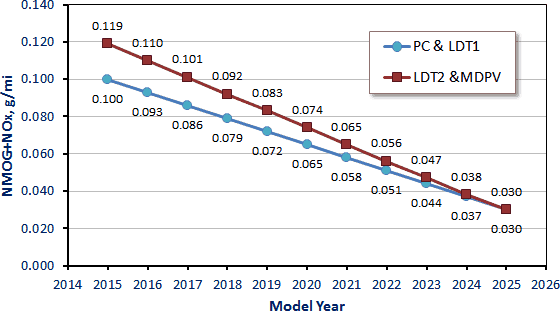
LDT1: 0-3750 lbs LVW. LDT2: 3751-8500 lbs LVW.
Medium-duty vehicles have no fleet average requirements. Rather, a phase-in schedule requires manufacturers to certify increasing percentages of their MDVs to increasingly more stringent emission categories. For diesel MDV, manufacturers can also choose to certify the engines to the applicable heavy-duty diesel engine emission standards.
Durability. The LEV III standards phase-in a new 150,000 miles durability requirement, compared to the LEV II 50,000 and 120,000 miles standards. Manufacturers receive a 5 mg/mi FTP NMOG credit for extended, 150,000 mile warranty coverage.
Evaporative Emissions. All light-duty vehicles would have to meet a more stringent “zero” evaporative standard, while using more challenging test fuels, such as E10.
Direct Ozone Reduction Credit. Manufacturers receive an NMOG credit for direct ozone reduction systems (such as ozone reducing catalysts coated on vehicle radiators). The in-use performance of the system must be monitored via an OBD strategy.
Low Emission Vehicle IV (LEV IV) Standards
The LEV IV emission standards were finalized by CARB in August 2022 and approved by the Office of Administrative Law (OAL) in November 2022 [5696]. They are phased-in over the 2026-2030 model years. Manufacturers can certify vehicles to the LEV IV standards in model year 2025 but beginning with model year 2026, all vehicles must be certified to LEV IV standards.
The LEV IV standards modify the LEV III standards in several ways including: (1) phase out the use of ZEVs and emission-adjusted PHEVs in the calculation of the combined NMOG+NOx fleet average requirement by the 2029 model year, (2) introduction of new bins including low emission bins and removal of high emission bins (4) introduction of high altitude NMOG+NOx limits, partial soak standards and quick drive-away standards, (6) introduction of fleet standards for medium-duty vehicles.
LEV IV emission categories and their FTP-75 standards for light- and (chassis-certified) medium-duty vehicles are listed in Table 9. The PM limits and phase-in are consistent with the LEV III requirements summarized in Table 7. Under proposed ACC II amendments, the PM limits for both light- and medium-duty vehicles are to be lowered to 0.5 mg/mi to harmonize with the EPA Tier 4 regulation.
A manufacturer has the option of certifying engines used in incomplete MDVs greater than 10,000 lbs GVWR and all diesel engine MDVs greater than 10,000 lbs GVWR to the heavy-duty engine standards.
| Vehicle Type | Emission Category | NMOG+NOx* | CO | HCHO | PM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g/mi | g/mi | mg/mi | mg/mi | ||
| All PCs LDTs ≤ 8500 lbs GVWa All MDPVs |
ULEV125 | 0.125/0.160 | 4.2 | 4 | 1a |
| ULEV70 | 0.070/0.105 | 2.1 | |||
| ULEV60 | 0.060/0.090 | 1.7 | |||
| ULEV50 | 0.050/0.070 | 1.7 | |||
| ULEV40 | 0.040/0.060 | 1.7 | |||
| SULEV30 | 0.030/0.050 | 1.0 | |||
| SULEV25 | 0.025/0.050 | 1.0 | |||
| SULEV20 | 0.020/0.030 | 1.0 | |||
| SULEV15 | 0.015/0.030 | 1.0 | |||
| MDVs 8501 - 10,000 lbs GVW | ULEV250 | 0.250 | 6.4 | 6 | 8 |
| ULEV200 | 0.200 | 4.2 | |||
| SULEV170 | 0.170 | 4.2 | |||
| SULEV150 | 0.150 | 3.2 | |||
| SULEV125 | 0.125 | 3.2 | |||
| SULEV100 | 0.100 | 3.2 | |||
| SULEV85 | 0.085 | 3.2 | |||
| SULEV75 | 0.075 | 3.2 | |||
| MDVs 10,001 - 14,000 lbs GVW | ULEV400 | 0.400 | 7.3 | 6 | 10 |
| ULEV270 | 0.270 | 4.2 | |||
| SULEV230 | 0.230 | 4.2 | |||
| SULEV200 | 0.200 | 3.7 | |||
| SULEV175 | 0.175 | 3.7 | |||
| SULEV150 | 0.150 | 3.7 | |||
| SULEV125 | 0.125 | 3.7 | |||
| SULEV100 | 0.100 | 3.7 | |||
|
* Low/high altitude or low altitude a Phased in 2026 to 2028: 50% in 2026, 75% in 2027 and 100% in 2028 vehicles must meet the 1 mg/mi limit. Remaining vehicles must meet a 3 mg/mi limit. | |||||
Other testing requirements apply to LEV IV vehicles, Table 10. For LDVs, these include partial soak standards, quick drive-away standards, 50°F (10°C) standards, cold CO standards, US06 standards, High Power Cold Start Standards for Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV), SC03 standards and HWFET standards. For MDVs, additional tests include 50°F (10°C) standards, SC03 standards, HWFET standards and SFTP standards. For MDVs with GVWR of 8501 to 10000 lbs, the SFTP test is carried out with the US06 cycle while for MDVs with GVWR of 10,001 to 14,000 lbs, the SFTP testing is carried out on the Hot 1435 UC cycle. Additionally, for MDVs with a GCWR greater than 14,000 lbs, Moving Average Window (MAW) testing requirements apply.
| Test | All PCs LDTs ≤ 8500 lbs GVW All MDPVs | MDVs 8501 - 10,000 lbs GVW | MDVs 10,001 - 14,000 lbs GVW |
|---|---|---|---|
| Partial soak NMOG+NOx | Full compliance by 2028; FUL | ||
| Quick drive-away NMOG+NOx | Full compliance by 2028; FUL | ||
| 50°F (10°C) NMOG+NOx and HCHO | Compliance starting 2026; Applies at 4,000 miles | Compliance starting 2026; Applies at 4,000 miles | |
| Cold CO | Compliance starting 2026; Applies at 50,000 miles | ||
| US06 NMOG+NOx, CO and PM | Full compliance of NMOG+NOx and CO by 2028; Vehicles not meeting final NMOG+NOx and CO limits in 2026 and 2027 must meet Interim standards; PM full compliance by 2030; Vehicles not meeting final 3 mg/mi PM limit in 2026 – 2029 must meet interim 6 mg/mi limit; FUL | Full compliance of NMOG+NOx and CO by 2029; Vehicles not meeting final NMOG+NOx and CO limits in 2026 – 2028 must meet LEV III SFTP limits; PM full compliance by 2029; Vehicles not meeting final PM limit in 2026 – 2028 must meet LEV III SFTP PM limit; FULa | |
| Hot 1435 UC NMOG+NOx, CO and PM | Full compliance of NMOG+NOx and CO by 2029; Vehicles not meeting final NMOG+NOx and CO limits in 2026 – 2028 must meet LEV III SFTP limits; PM full compliance by 2029; Vehicles not meeting final PM limit in 2026 – 2028 must meet LEV III SFTP PM limit; FUL | ||
| High power cold start US06 PHEV NMOG+NOx | PHEVs; full compliance by 2028; FUL | ||
| SC03 NMOG+NOx and CO | Compliance starting 2026; FUL | Compliance starting 2026; FUL | |
| HWFET NMOG+NOx | Compliance starting 2026; FUL | Compliance starting 2026; FUL | |
| MAW NMHC, NOx, CO and PM | All MDVs with GCWRb greater than 14,000 lbs | ||
|
a Full US06 for MDVs with hp/GVWR > 0.024; US06 Bag 2 for MDVs with hp/GVWR ≤ 0.024 b Gross Combined Weight Rating, includes the vehicle and its trailer | |||
Fleet Emission Requirements. Fleet NMOG+NOx requirements for PCs, LDTs and MDPVs remain at 0.030 g/mi from 2026 onward. However, the percentage of a manufacturer’s total ZEVs + emission-adjusted PHEVs allowed in the fleet calculation decreases to 0% by 2029, Table 11. Emission-adjusted PHEVs use a PHEV NMOG+NOx contribution factor that accounts for the all-electric driving range over the FTP and US06 cycles.
| Model Year | NMOG+NOx, g/mi | Maximum Percent ZEVs + emission-adjusted PHEVsa |
|---|---|---|
| 2025b | 0.030 | 100% |
| 2026 | 60% | |
| 2027 | 30% | |
| 2028 | 15% | |
| 2029+ | 0% | |
|
a For each model year, a manufacturer may only include up to the specified percentage of its total ZEVs + emission-adjusted PHEVs in the fleet average calculation b Only applicable to manufacturers optionally certifying 2025 model year test groups | ||
The fleet average requirements for MDVs are summarized in Table 12. ZEV are excluded from the fleet average calculation except for the 2025 model year.
| Model Year | NMOG+NOx, g/mi | |
|---|---|---|
| MDVs 8,501 to 10,000 lbs GVWR | MDVs 10,001 to 14,000 lbs GVWR | |
| 2025a | 0.178 | 0.247 |
| 2026 | 0.178 | 0.247 |
| 2027 | 0.174 | 0.232 |
| 2028 | 0.166 | 0.212 |
| 2029 | 0.158 | 0.193 |
| 2030+ | 0.150 | 0.175 |
| a Only applicable to manufacturers optionally certifying 2025 model year test groups. | ||