Audi launches new MHEV plus hybridization technology
28 January 2025
Audi has launched its first combustion engines with the new MHEV plus mild hybrid technology. The new hybrid platform will be available in the Audi A5 and Q5 series models built on the Premium Platform Combustion.
The MHEV plus technology will not be offered in the US market “due to differing customer needs”, Audi said in a press release.
MHEV plus offers such functions as partially electric driving, electric boosting, and a significant increase in efficiency and comfort, according to Audi. The mild hybrid system in the new Audi A5 and Q5 consists of three main components: a new powertrain generator (PTG) with integrated power electronics and a permanently excited synchronous motor (PSM), a 48 V battery, and a belt alternator starter (BAS).
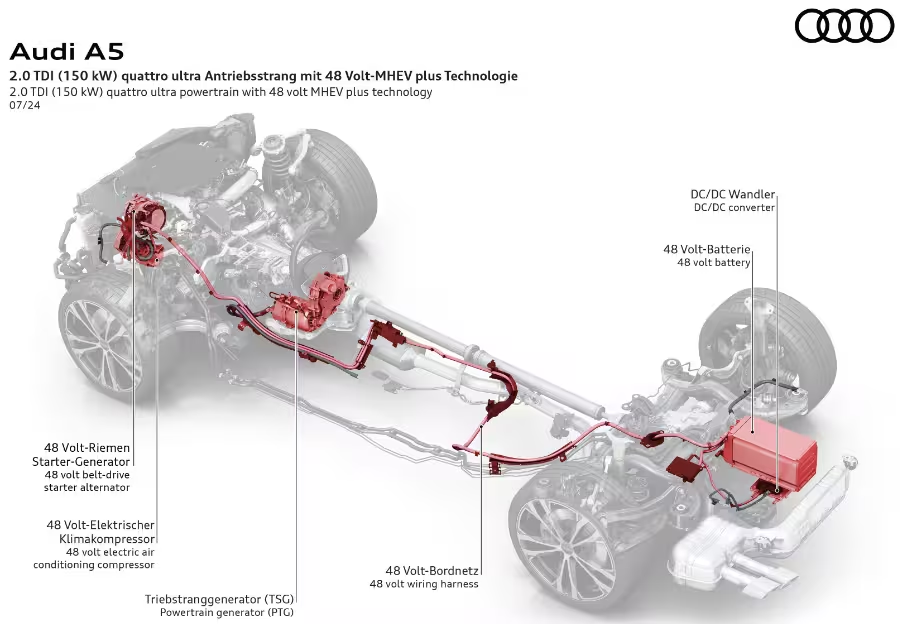
The architecture of the MHEV plus system can be integrated into various models with front and quattro (four-wheel drive) drivetrains based on the Premium Platform Combustion (PPC). Situation-specific liquid cooling of the power electronics and the electric motor enables the components to meet power and torque demands in all operating states. The MHEV plus technology enables purely electric operating states and can also support the combustion engine.
The system increases performance while reducing fuel consumption and CO2 emissions. For example, in the A5 2.0 TDI (150 kW front/quattro; combined fuel consumption: 5.7–4.8 L/100 km; CO2 emissions: 150–125 g/km), the respective savings are up to 0.38 L/100 km or 10 g/km. In the 3.0 TFSI with V6 engine (270 kW quattro; fuel consumption: 8.0–7.4 l/100 km; CO2 emissions: 182–169 g/km), the respective savings are up to 0.74 L/100 km or 17 g/km.
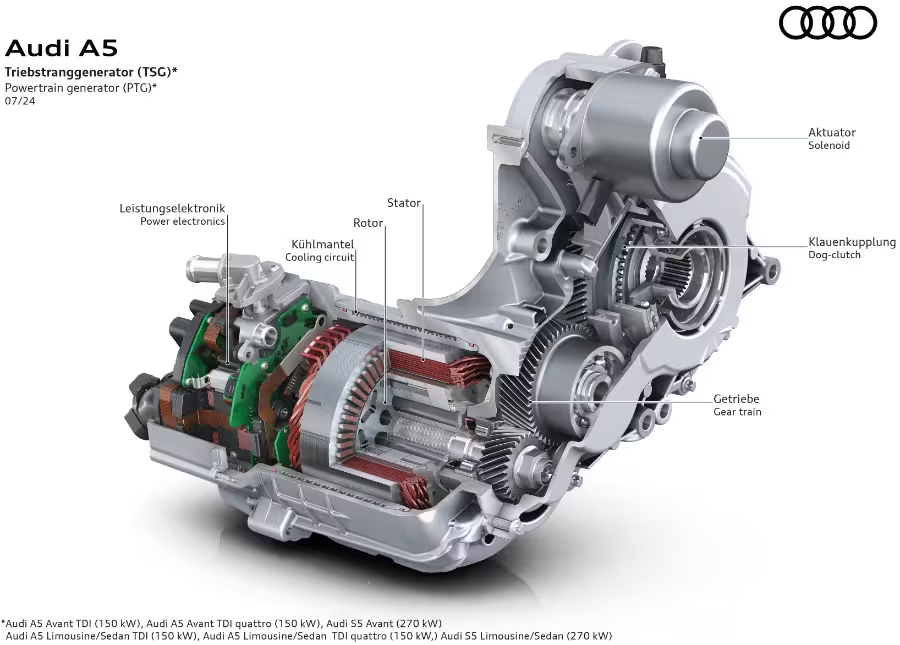
The electric drive module in the new MHEV plus system is the powertrain generator (PTG). This component also represents the biggest difference to the MHEV technology previously offered by Audi, which worked exclusively with a belt-driven alternator starter.
The PTG, which is installed in a compact unit with integrated power electronics directly on the output shaft of the transmission, can contribute up to 18 kW (24 PS) of electrical power to the drive. The module enables a maximum torque of 230 Nm at the transmission output, which is already available as drive torque when the vehicle is started. The PTG’s transmission operates with a ratio of 3.6:1. MHEV plus utilizes the PTG up to a maximum speed of 140 km/h for maximum efficiency. At higher vehicle speeds, the PTG disengages from the drivetrain via an integrated dog clutch.
The PTG weighs around 21 kg and enables a maximum of 5,550 rpm on the output shaft. Depending on the vehicle and drive variant, this corresponds to a speed of 130 to 140 km/h.
The positioning of the PTG directly behind the gearbox offers several advantages: the 18 kW of drive power or up to 25 kW of power from regenerative braking supplied by the PTG is available directly at the axle output without further losses. Due to this configuration, the PTG can be used in both front-wheel and all-wheel drive vehicles without any modifications and in a modular fashion.
The conventional drivetrains available with first-generation start-stop or mild hybridization relied on key efficiency components such as engine stop when the vehicle is at a standstill, coasting, freewheeling with the engine off, and 12 V or 48 V energy recovery. The main advantages of the new technology include the added convenience of start-stop operation, emission-free coasting, energy recovery, partially electric driving (for example for electric parking and maneuvering), and increased performance thanks to the electric support of the combustion engine.
As part of the MHEV plus technology, the belt alternator starter (BAS) is tasked with starting the engine and delivering electrical energy to the battery. The belt alternator starter can also recover the engine’s energy when it is switched off and places the cylinders in the optimum position for restarting.
The lithium-ion battery made with lithium iron phosphate (LFP) has a storage capacity of 37 Ah, which corresponds to just under 1.7 kWh (gross). Its maximum discharge power is 24 kW. Due to the requirements for availability, power, and torque, the battery is integrated into a low-temperature water-cooling circuit that ensures optimum conditions in the range of 25 to 60°C. This is the first time that Audi is using an LFP battery for its mild hybrid systems.
The integrated brake control system (iBRS) plays an important role in energy recovery. In models with MHEV plus technology, iBRS ensures pressure-free braking and achieves the necessary deceleration through regenerative braking without the use of the mechanical wheel brake. Mechanical brakes are only applied when the brake pedal is depressed more forcefully.
Models with MHEV plus can also run purely electrically, for example when the vehicle is approaching a town, and can then maintain its speed with the help of the PTG. If the power required by the driver or the Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) exceeds a certain value, the combustion engine starts up and takes over propulsion. The start-up threshold depends on the current SoC of the 48 V battery and the speed of the vehicle.
Source: Audi